
When a "channel up" or "channel down" input is given to it, the sequential logic of the channel selection circuitry calculates the new channel from the input and the current channel.ĭigital sequential logic circuits are divided into synchronous and asynchronous types. The television stores the current channel as part of its state. In order for the channel selection to operate correctly, the television must be aware of which channel it is currently receiving, which was determined by past channel selections. However, if the television is on channel 8, pressing "up" switches it to channel "9". If the television is on channel 5, pressing "up" switches it to receive channel 6.
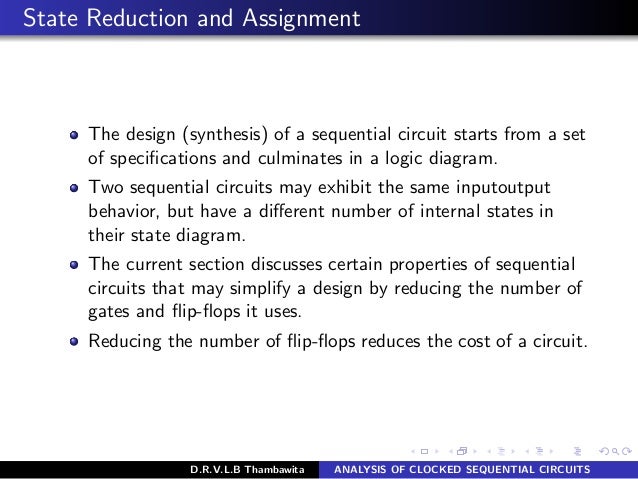
Pressing the "up" button gives the television an input telling it to switch to the next channel above the one it is currently receiving. Virtually all circuits in practical digital devices are a mixture of combinational and sequential logic.Ī familiar example of a device with sequential logic is a television set with "channel up" and "channel down" buttons. Sequential logic is used to construct finite-state machines, a basic building block in all digital circuitry. That is, sequential logic has state ( memory) while combinational logic does not. This is in contrast to combinational logic, whose output is a function of only the present input. In automata theory, sequential logic is a type of logic circuit whose output depends on the present value of its input signals and on the sequence of past inputs, the input history. For the synthesizer company, see Sequential Circuits.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
